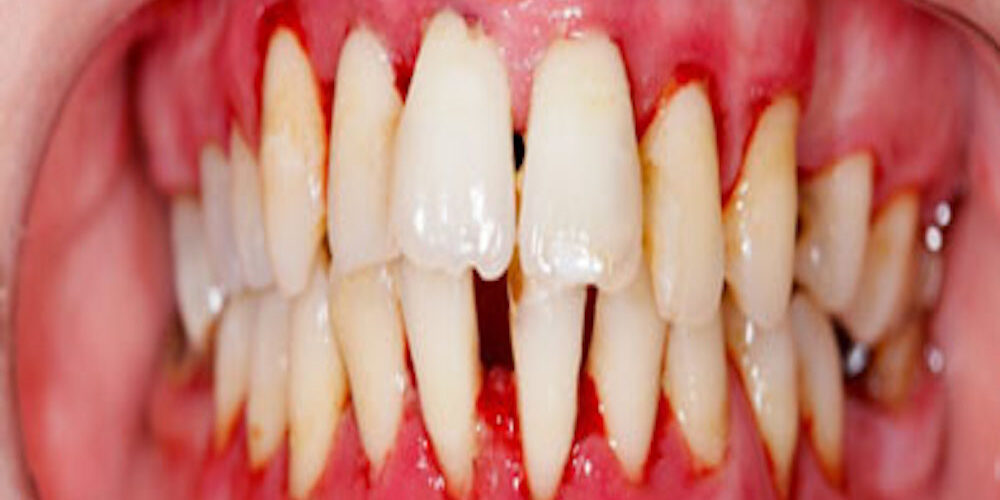
Periodontal disease or Gum disease is a pathological condition where the gum and supporting structures like the soft tissues (periodontal tissues) and bone surrounding the teeth are inflamed. The Gingivitis and Periodontitis are the most common periodontal diseases.

Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums and is the initial stage of gum disease. It is characterized by inflamed gums, redness of the gum margins, swelling and bleeding on brushing. It can be acute or chronic.
Acute gingivitis is usually associated with specific infections or bacteria or trauma. Chronic gingivitis on the other hand, is the inflammation of the gum and surrounding structures of the teeth due to plaque accumulation of the teeth and gums. Gingivitis can be reverse with proper oral care.

Periodontitis is the inflammation of the gums affecting the soft tissues and bone surrounding the teeth resulting in pocket formation. It may progress or worsen resulting in mobile teeth or loss of teeth. Not all gingivitis progress into periodontal disease but progression to periodontal disease is influenced by number of factors.

Factors like poor oral hygiene, systemic diseases like diabetes, habits like smoking, genetic predisposition, medications like antihypertensive drugs, etc are predisposing factors. Diet also impacts on periodontal health. Acute necrotising ulcerative gingivitis occurs in smokers. Although irreversible periodontal disease may respond to treatment and can be halted.
Aims of Periodontal Surgery
- Regeneration of the lost bones and tissues
- Prevent mobile or tooth loss
- Reduce pocket formation or gaps between teeth (black triangles)
- Eliminate bacteria and infection

Periodontal tissue has the capacity to regeneration and repair. Hence, Periodontal surgery is done to eliminate inflammation and destruction of the gums and surrounding structures like the soft tissues and bone and regenerate them if possible. Advances in technology and innovation for the last few decade helps in understanding the factors like migration, attachment and proliferation of cells. Regeneration of the periodontal tissues is a process in which cell and extracellular matrix interactions occurs.
Growth factors are naturally occurring proteins with various local properties like speeds up wound healing, tissues regeneration, etc. Certain growth hormones like Polypeptide growth factors (PFGs), fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin like growth factors (IGFs), transforming growth factors (TGFs), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), etc plays an important role in periodontal surgery.

The FGF has chemotactic and mitogenic effects to endothelial cells and variety of mesenchymal cells like fibroblasts, osteoblasts, chondrocytes, smooth muscle cells, skeletal myoblasts, etc and stimulate angiogenesis and neovascularization. It also stimulates cells in G0 to G1 in cell cycle and promote healing of fractures by stimulating growth and biochemical functions.

Polypeptide growth factors (PFGs) is a naturally occurring growth factors which play an important role in tissue repair like cell proliferation, chemotaxis, differentiation and matrix synthesis.
EGF is a multifunctional growth factor with numerous functions in epithelial growth and differentiation, wound healing, stimulate DNA synthesis and cell growth in various cells of epithelial, endothelial and mesodermal origin.
TGF is a growth factor which has two forms, TGF-α and TGF-β. It helps in cell replication, differentiation and can alter the cellular response of other growth factors like PDGF, EGF, etc. It also speed up wound healing and formation of granulation tissue, fibroblasts and capillaries.
PDGF stimulates cells proliferation and chemotaxis to various mesenchymal cells and shows cells adhesion. Studies show bone regeneration in furcation defects and gingival recession sites.

Platelet rich plasma or Platelet rich fibrin are generations of Platelets which contains growth factors, cytokines, etc and they stimulate adhesion, aggregation, migration of fibroblasts and stem cells. They also enhanced wound healing, formation of granulation tissues in the defect site, etc.
Conclusion

Better understanding of growth factors, mechanisms of action and molecular pathways help in applying growth factors at targeted specific area and apply these combination techniques into healing and stopping the diseases in the near future.